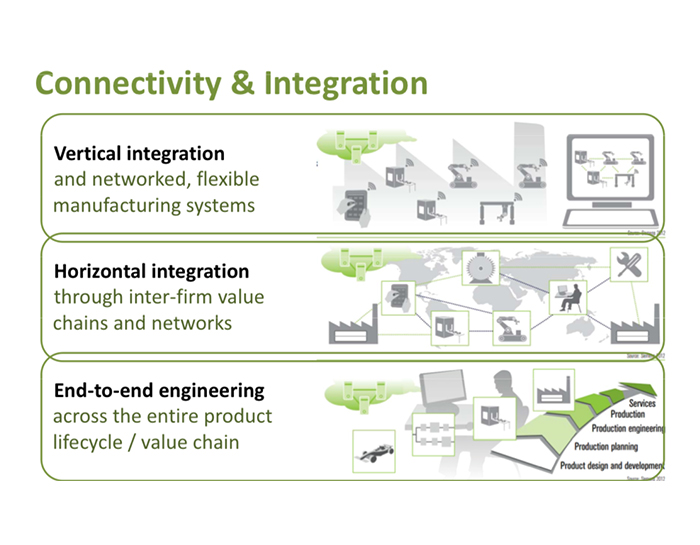
The emergence of Industry 4.0 will be followed by Digital Production, which will transform the manufacturing process as we know it today. This means physical production, through cloud computing, will be connected to digital systems and other players in the supply chain. Digital production will enable the virtual manufacture of products, sense potential issues and communicate these problems to the system, as well as choose the optimal way to manufacture products.
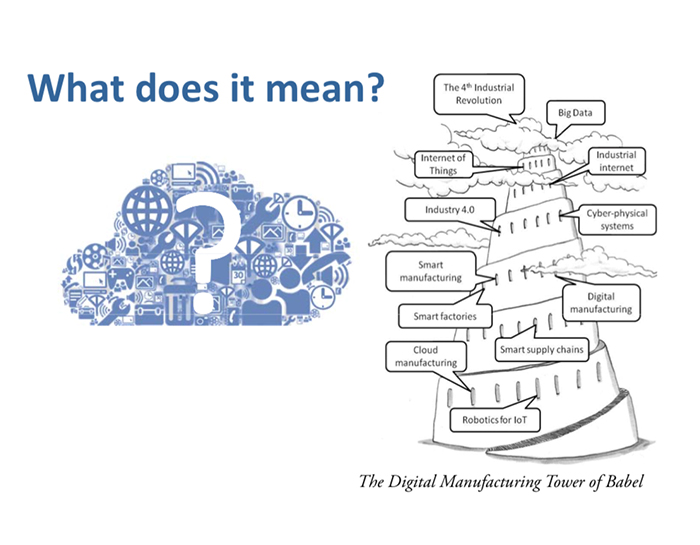
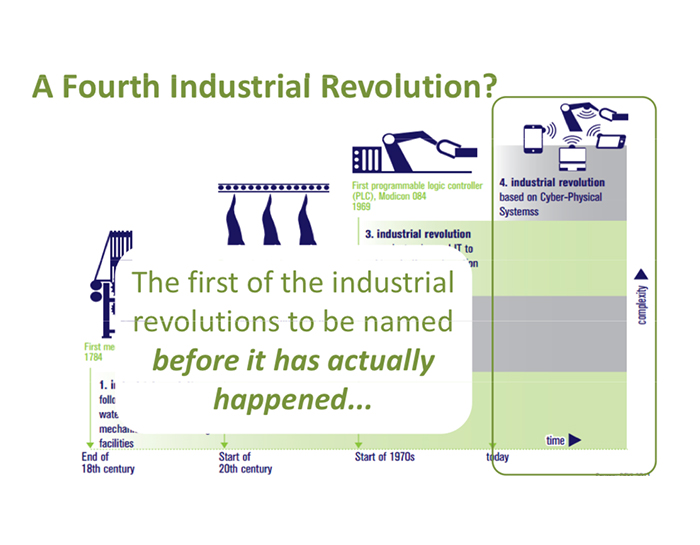
The industrial revolution we’re experiencing now, commonly referred to as Industry 4.0, is powered by advancements that include smart manufacturing, robotics, artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT). In addition to prompting manufacturers to invest $267 billion in the IoT by 2020, Industry 4.0 is revolutionizing manufacturing along five dimensions:
- Seeing Around Corners – in 360°: New tools are allowing companies to create and test situations in the virtual world, to simulate the design process and the assembly line before an actual product is created. Simulating the product-creation phase helps cut down on manufacturing time and ensure the manufacturing process delivers what companies intended to create.
- Viewing the Fourth Wave – in 3D: Also, making a mark in the manufacturing world is 3-D printing, which allows for the seamless creation of tangible products using a single machine. This is a fundamental change, because it gives you a lot more possibilities for how you design a part. For a certain category of product where you would normally need six pieces, 3-D printing can achieve the same thing in one piece without additional processes like welding or screwing. Three-dimensional printing reduces waste by recycling plastic and cuts down on the wait time for replacement parts and transportation. Its implications for mass production are various, making advancements possible in products ranging from toys to medical devices.
- Advanced Manufacturing – on Autopilot: Automation is another vital aspect of the industry’s future. Approximately 50% of Flex’s manufacturing processes are already fully automated. Automation enables a level of accuracy and productivity beyond human ability—even in environments that would be considered unsafe for humans. The new generation of robotics is not only much easier to program, but easier to use, with capabilities like voice and image recognition to re-create complex human tasks.
- Building Intelligent Factories – in the Cloud: In addition to robotics and virtual reality, factories environments are also driving advancements in cloud computing and smart sensors. Smart sensors can perform tasks such as converting data into different units of measurement, communicating with other machines, recording statistics and feedback and shutting off devices if a safety or performance issue arises. IoT functionality can track and analyze production quotas, consolidate control rooms and create models of predictive maintenance.
- Robots on the Rise – Managed by Humans: Building a better manufacturing sector with augmented and virtual reality, robotics and data analysis using smart equipment naturally raises an important question: What will the Industry 4.0 workforce look like? While there are still some significant challenges ahead, the outlook is strong despite the obvious concern of robots displacing jobs. The bulk of automation is used for work that would be considered unsafe or impossible for humans. This makes robots a complement to, not a replacement for, human workers. Because of robots, we’ll be able to increase our output.